基本 CRUD 应用程序
虽然在基本的 CRUD 应用程序中使用 Socket.IO(或纯 WebSocket)听起来有点过分,但轻松通知所有用户的能力确实很强大。
在本指南中,我们将基于出色的 TodoMVC 项目 创建一个基本的 CRUD(代表 **C**reate/ **R**ead/ **U**pdate/ **D**elete)应用程序。
我们将涵盖以下主题
让我们开始吧!
安装
代码可以在主存储库的 examples 目录中找到
git clone https://github.com/socketio/socket.io.git
cd socket.io/examples/basic-crud-application/
您应该看到两个目录
运行前端
该项目是一个基本的 Angular 应用程序,它是使用 Angular CLI 创建的。
要运行它
cd angular-client
npm install
npm start
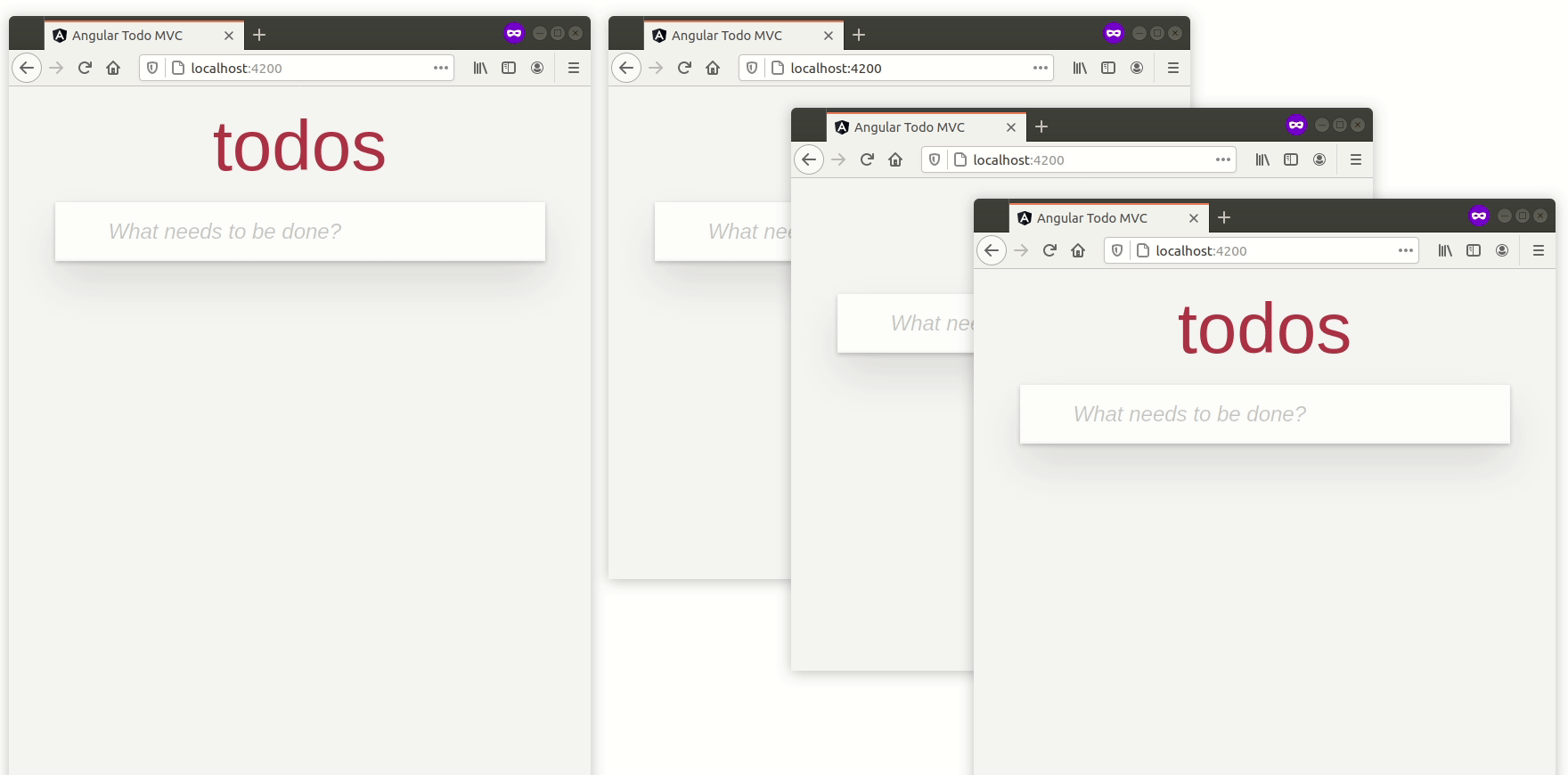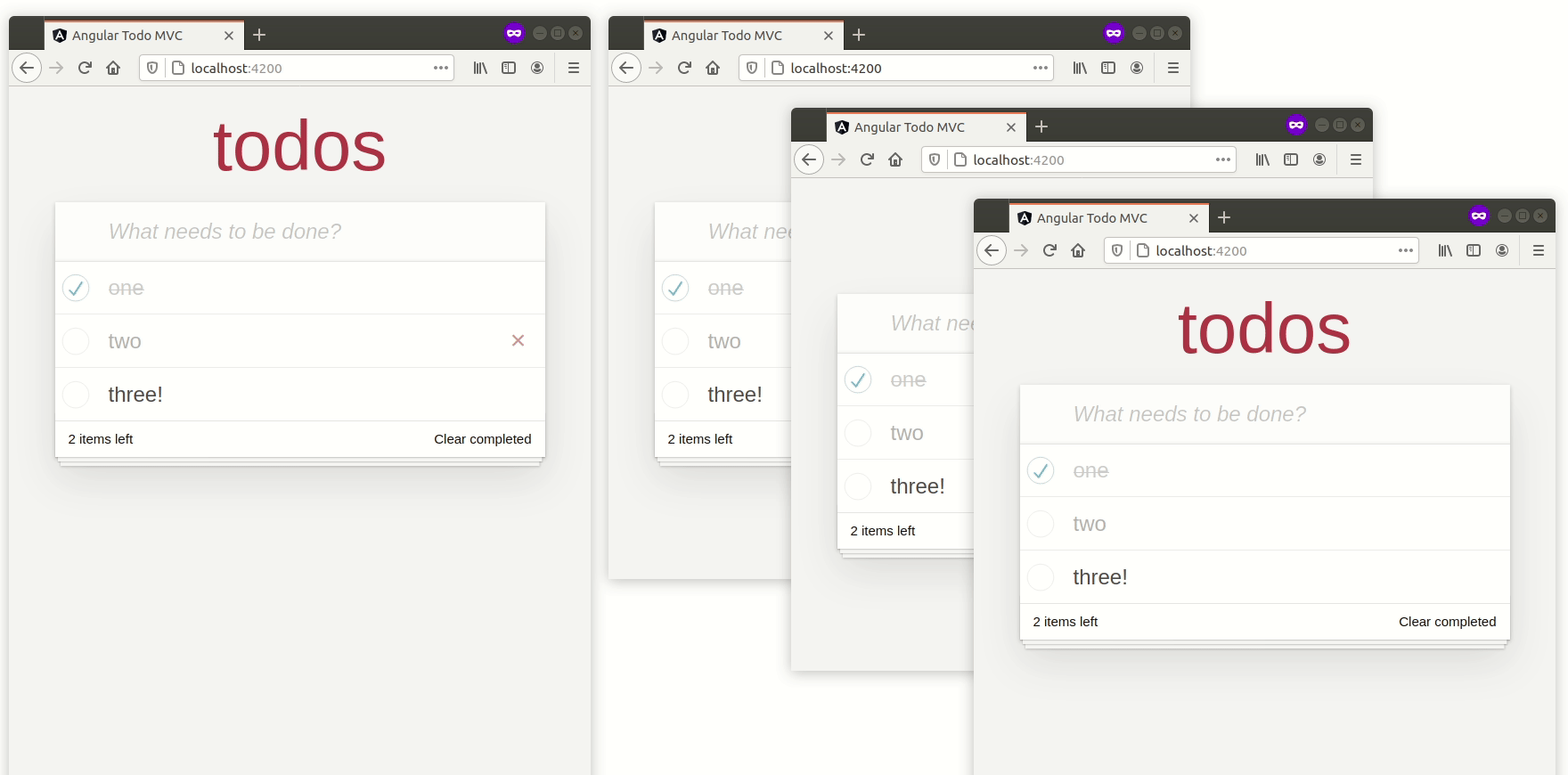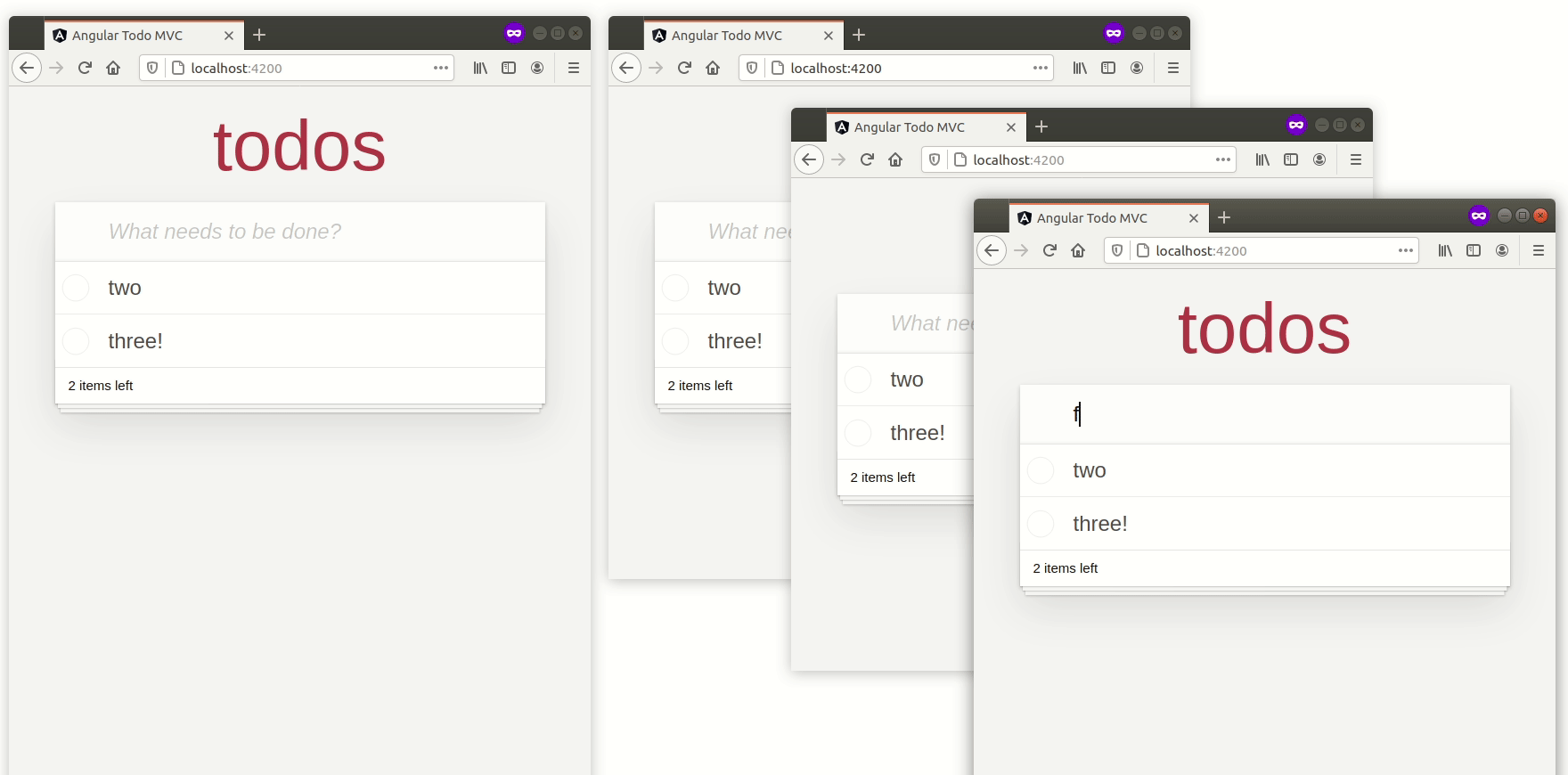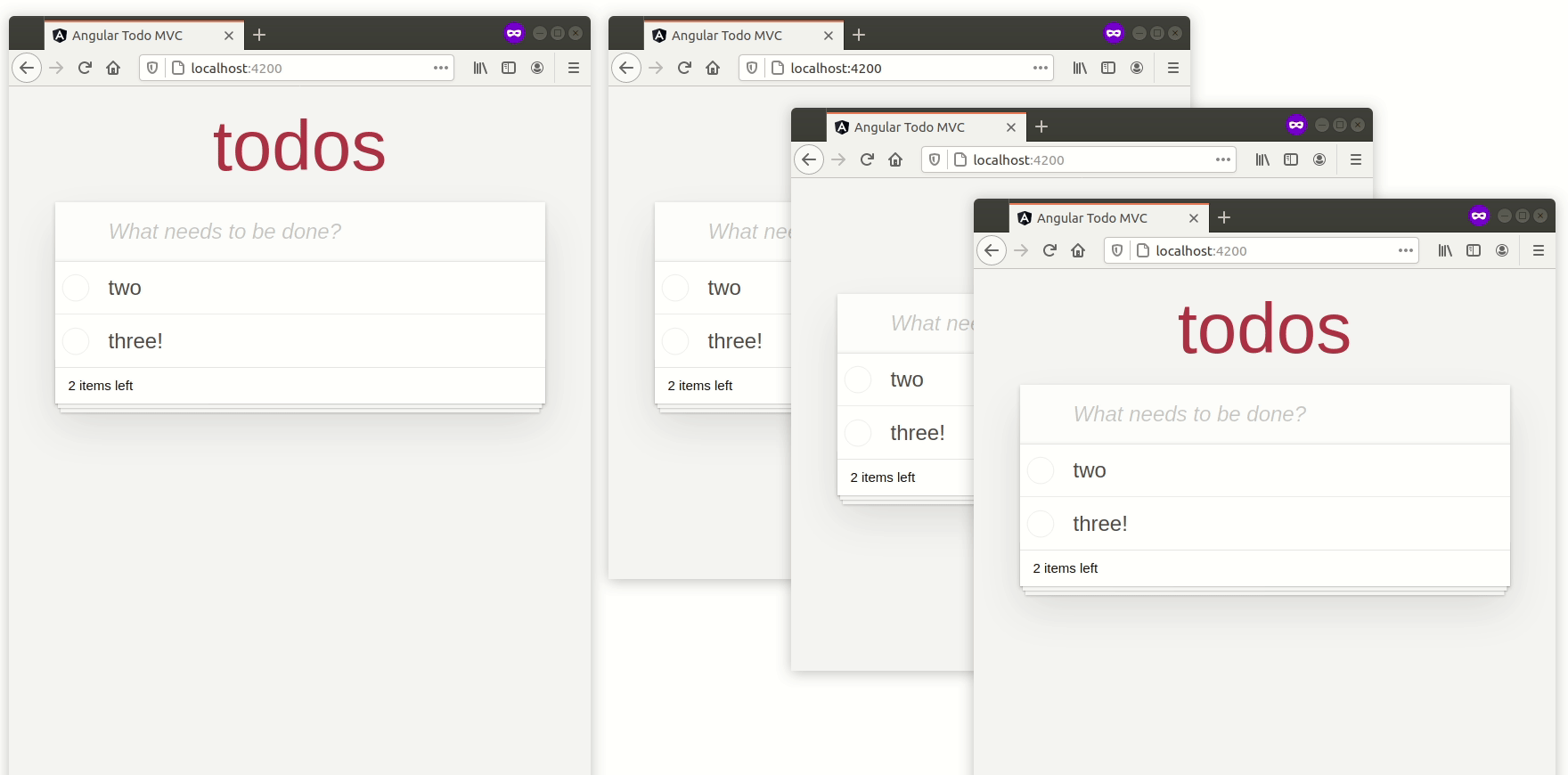
然后,如果您在浏览器中打开 https://:4200,您应该看到
到目前为止,一切都很好。
运行服务器
现在让我们关注服务器
cd ../server
npm install
npm start
您现在可以打开多个选项卡,并且待办事项列表应该神奇地在它们之间同步

工作原理
服务器结构
├── lib
│ ├── index.ts
│ ├── app.ts
│ ├── todo-management
│ │ ├── todo.handlers.ts
│ | └── todo.repository.ts
│ └── util.ts
├── package.json
├── test
│ └── todo-management
│ └── todo.tests.ts
└── tsconfig.json
让我们详细说明每个文件的职责
index.ts:服务器的入口点,它创建组件并初始化应用程序app.ts:应用程序本身,在其中创建 Socket.IO 服务器,并注册处理程序todo.handlers.ts:对 Todo 实体的操作的处理程序todo.repository.ts:用于从数据库持久化/检索 Todo 实体的存储库util.ts:项目中使用的一些通用实用程序方法todo.tests.ts:集成测试
初始化
首先,让我们关注 lib/app.ts 文件中的 createApplication 方法
const io = new Server<ClientEvents, ServerEvents>(httpServer, serverOptions);
我们使用以下选项创建 Socket.IO 服务器
{
cors: {
origin: ["https://:4200"]
}
}
因此,在 https://:4200 上提供服务的 Frontend 应用程序被允许连接。
文档
<ClientEvents, ServerEvents> 部分特定于 TypeScript 用户。它允许显式指定在服务器和客户端之间交换的事件,因此您获得自动完成和类型检查
回到我们的应用程序!然后,我们通过注入应用程序组件来创建处理程序
const {
createTodo,
readTodo,
updateTodo,
deleteTodo,
listTodo,
} = createTodoHandlers(components);
我们注册它们
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.on("todo:create", createTodo);
socket.on("todo:read", readTodo);
socket.on("todo:update", updateTodo);
socket.on("todo:delete", deleteTodo);
socket.on("todo:list", listTodo);
});
文档:监听事件
注意:事件后缀(:create、:read 等)在 REST API 中替换了通常的 HTTP 动词
POST /todos=>todo:createGET /todos/:id=>todo:readPUT /todos/:id=>todo:update- ...
事件处理程序
现在让我们关注 lib/todo-management/todo.handlers.ts 文件中的 createTodo 处理程序
首先,我们检索 Socket 实例
createTodo: async function (
payload: Todo,
callback: (res: Response<TodoID>) => void
) {
const socket: Socket<ClientEvents, ServerEvents> = this;
// ...
}
请注意,使用箭头函数 (createTodo: async () => {}) 在这里不起作用,因为 this 不会指向 Socket 实例。
然后,我们使用出色的 joi 库验证有效负载
const { error, value } = todoSchema.tailor("create").validate(payload, {
abortEarly: false, // return all errors and not just the first one
stripUnknown: true, // remove unknown attributes from the payload
});
如果有验证错误,我们只需调用确认回调并返回
if (error) {
return callback({
error: Errors.INVALID_PAYLOAD,
errorDetails: error.details,
});
}
我们在客户端处理错误
// angular-client/src/app/store.ts
this.socket.emit("todo:create", { title, completed: false }, (res) => {
if ("error" in res) {
// handle the error
} else {
// success!
}
});
文档:确认
如果有效负载成功匹配模式,我们可以生成一个新的 ID 并持久化实体
value.id = uuid();
try {
await todoRepository.save(value);
} catch (e) {
return callback({
error: sanitizeErrorMessage(e),
});
}
如果出现意外错误(例如,如果数据库已关闭),我们使用通用错误消息调用确认回调(为了不公开应用程序的内部机制)。
否则,我们只需使用新 ID 调用回调
callback({
data: value.id,
});
最后(这是神奇的部分),我们通知所有其他用户创建
socket.broadcast.emit("todo:created", value);
文档:广播事件
在客户端,我们为该事件注册一个处理程序
// angular-client/src/app/store.ts
this.socket.on("todo:created", (todo) => {
this.todos.push(mapTodo(todo));
});
就是这样!
测试
由于我们是相当合理的开发人员,我们现在将为我们的处理程序添加一些测试。让我们打开 test/todo-management/todo.tests.ts 文件
应用程序在 beforeEach 钩子中创建
beforeEach((done) => {
const partialDone = createPartialDone(2, done);
httpServer = createServer();
todoRepository = new InMemoryTodoRepository();
createApplication(httpServer, {
todoRepository,
});
// ...
});
我们创建两个客户端,一个用于发送有效负载,另一个用于接收通知
httpServer.listen(() => {
const port = (httpServer.address() as AddressInfo).port;
socket = io(`https://:${port}`);
socket.on("connect", partialDone);
otherSocket = io(`https://:${port}`);
otherSocket.on("connect", partialDone);
});
重要说明:这两个客户端在 afterEach 钩子中显式断开连接,因此它们不会阻止进程退出。
文档:https://mocha.node.org.cn/#hooks
我们的第一个测试(快乐路径)非常简单
describe("create todo", () => {
it("should create a todo entity", (done) => {
const partialDone = createPartialDone(2, done);
// send the payload
socket.emit(
"todo:create",
{
title: "lorem ipsum",
completed: false,
},
async (res) => {
if ("error" in res) {
return done(new Error("should not happen"));
}
expect(res.data).to.be.a("string");
// check the entity stored in the database
const storedEntity = await todoRepository.findById(res.data);
expect(storedEntity).to.eql({
id: res.data,
title: "lorem ipsum",
completed: false,
});
partialDone();
}
);
// wait for the notification of the creation
otherSocket.on("todo:created", (todo) => {
expect(todo.id).to.be.a("string");
expect(todo.title).to.eql("lorem ipsum");
expect(todo.completed).to.eql(false);
partialDone();
});
});
});
让我们也使用无效的有效负载进行测试
describe("create todo", () => {
it("should fail with an invalid entity", (done) => {
const incompleteTodo = {
completed: "false",
description: true,
};
socket.emit("todo:create", incompleteTodo, (res) => {
if (!("error" in res)) {
return done(new Error("should not happen"));
}
expect(res.error).to.eql("invalid payload");
// check the details of the validation error
expect(res.errorDetails).to.eql([
{
message: '"title" is required',
path: ["title"],
type: "any.required",
},
]);
done();
});
// no notification should be received
otherSocket.on("todo:created", () => {
done(new Error("should not happen"));
});
});
});
您可以使用 npm test 运行完整的测试套件
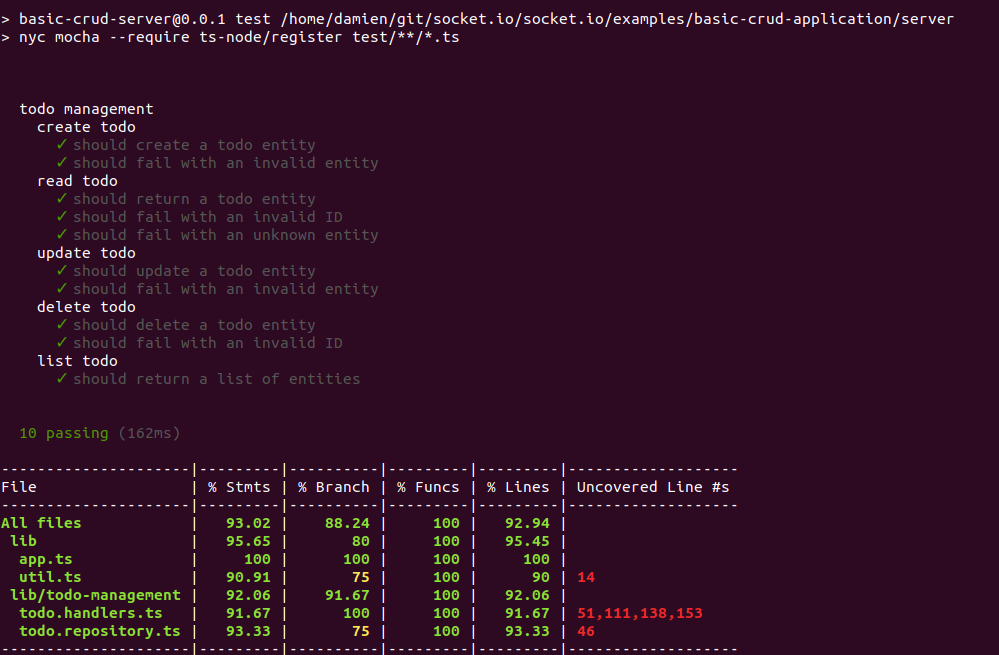
就这样!其他处理程序与第一个处理程序非常相似,这里不再赘述。
下一步
感谢您的阅读!